Eating healthy is easier said than done because there are a lot of products on the market that may be deceiving. Many food products may seem healthy, but are actually loaded with ingredients that are detrimental to your health. As part of a healthy diet, it’s important to include fruits and vegetables to your plate. Eating healthy can have many beneficial effects on the mind and body.
What to eat:
Adding colorful fruits and vegetables to your plate is beneficial for your health and increases life longevity. Colorful vegetables that contain phytonutrients protects humans from chronic diseases, such as heart disease, and reduces the risk of cancer. A balance of colorful fruits and veggies are of equal importance, where one specific color of fruit or vegetable is not necessarily more beneficial over the other. It’s also important to consume the skin of most fruits, such as apples or peaches, rather than peeling off the outer layers. When shopping for food, if you notice that your vegetables are mostly green, try adding in some colorful components to boost your intake of phytonutrients.
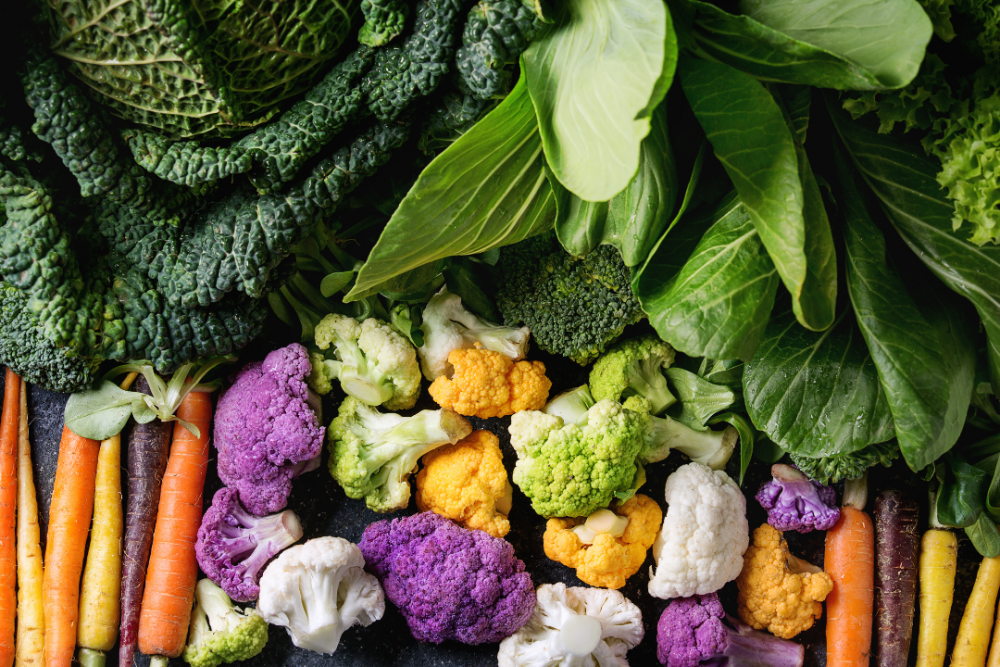

Phytonutrients in each color
Red
- Phytonutrient: carotenoid lycopene
- Benefits: protects against prostate cancer, along with heart and lung disease
- Most commonly found in: strawberries, cranberries, raspberries, tomatoes, cherries, apples, beets, watermelon, red grapes, red peppers, red onions
Orange and yellow
- Phytonutrient: beta cryptothanxin
- Benefits: prevent heart disease
- Most commonly found in: carrots, sweet potatoes, yellow peppers, oranges, bananas, pineapple, tangerines, mango, pumpkin, apricots, winter squash (butternut, acorn), peaches, cantaloupe, corn
Green
- Phytonutrient: sulforaphane, isocyanate, and indoles
- Benefits: inhibit action of carcinogens
- Most commonly found in: spinach, avocados, asparagus, artichokes, broccoli, alfalfa sprouts, kale, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, kiwi fruit, collard greens, green tea, green herbs (mint, rosemary, sage, thyme, and basil)
Blue and purple
- Phytonutrient: anthocyanins
- Benefits: antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-obesity effects, cardiovascular disease prevention
- Most commonly found in: blueberries, blackberries, elderberries, Concord grapes, raisins, eggplant, plums, figs, prunes, lavender, purple cabbage
White and Brown
- Phytonutrient: allicin, quercetin, and kaempferol
- Benefits: anti-tumor and antioxidants
- Most commonly found in: onions, cauliflower, garlic, leeks, parsnips, daikon radish, mushrooms
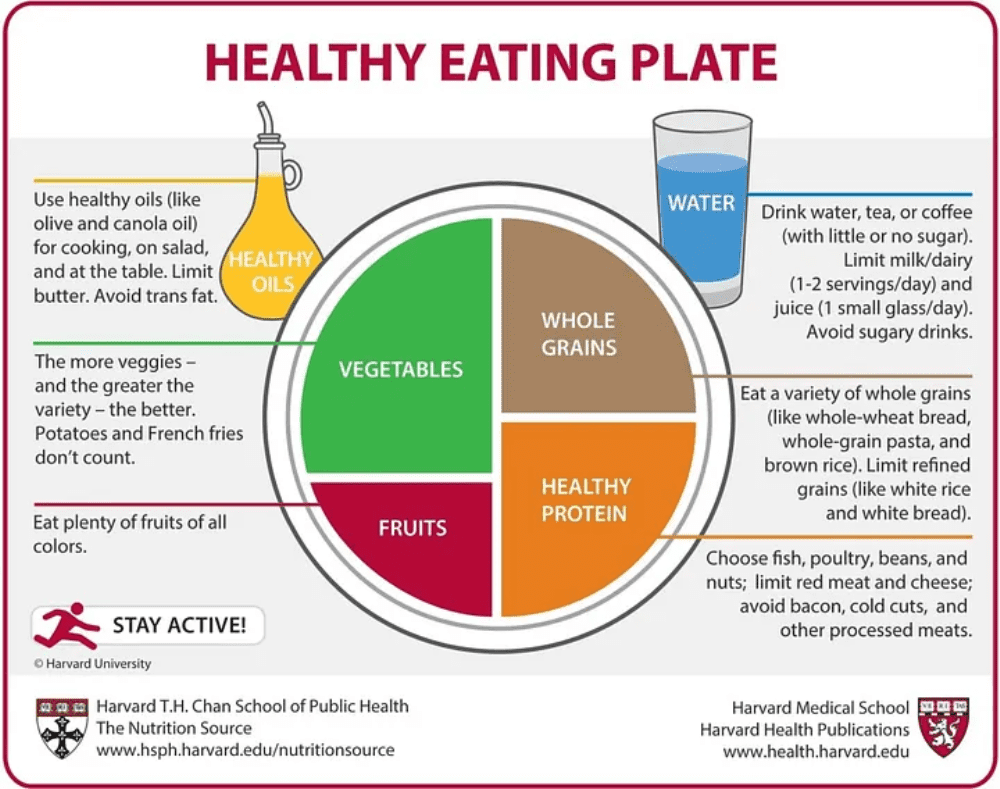
What not to eat:
Knowing what foods not to eat is just as important as knowing which foods to add on your plate. It’s best to avoid foods that have a high content in sugar, fat, and salt. Avoid sugar, salt, oils, fats and other additives. Highly processed foods are linked to obesity, type II diabetes, heart disease, and other problems. In addition, high cholesterol foods lead to an excess of plaque in the arteries. If there is a large accumulation of plaque in your arteries, it could lead to a heart attack or stroke.
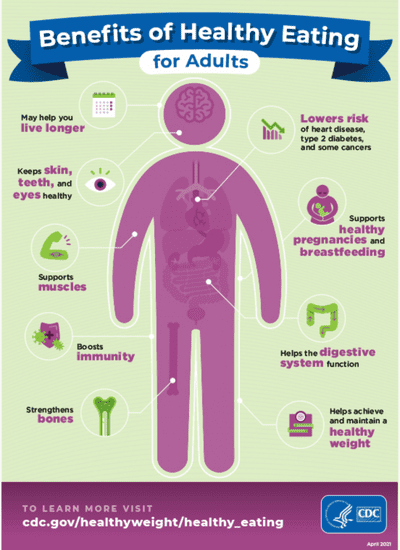
Eating healthy food is very beneficial for the overall wellness of your mind and body.
Healthy eating is important to prevent heart disease, promote better sleep, enhance gut health, and much more. If you struggle with healthy eating, we offer nutritional counseling, emotional eating therapy sessions, weight loss programs and more!
References
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, May 16). Benefits of healthy eating.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
-
https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/resources-publications/benefits-of-healthy-eating.html
-
Kahn, J. (2019, February 17). Picture perfect nutrition in 5 minutes: Food plates to use. Medium.
-
https://kahn642.medium.com/picture-perfect-nutrition-in-5-minutes-food-plates-to-use-48efaddc9669
-
Katherine D. McManus, M. S. (2019, April 25). Phytonutrients: Paint your plate with the colors of the rainbow.
-
Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/phytonutrients-paint-your-plate-with-the-colors-of-the-rainbow-2019042516501
-
Khoo, H. E., Azlan, A., Tang, S. T., & Lim, S. M. (2017, August 13). Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food & nutrition research.
-
MediLexicon International. (n.d.). Benefits of eating healthy: Heart health, Better Mood, and more.
-
Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322268
-
World Health Organization. (n.d.). Healthy diet. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/initiatives/behealthy/healthy-diet#:~:text=A%20healthy%20diet%20is%20essential,are%20essential%20for%20healthy%20diet.

